
Mastering Pool Care: Understanding and Learning Water Chemistry for Residential Swimming Pools
Mastering Pool Care: Understanding and Learning Water Chemistry for Residential Swimming Pools
Maintaining the right water chemistry is key to a safe and enjoyable residential swimming pool. This guide will help you with understanding and learning water chemistry for residential swimming pools, covering essentials like crucial chemicals, testing methods, balancing techniques, and troubleshooting tips. Let’s dive into the basics and keep your pool in top condition.
Key Takeaways
Balancing pool water chemistry is essential for preventing damage to surfaces and equipment while ensuring a safe and enjoyable swimming experience.
Regular testing and adjustment of chemical levels, including pH, alkalinity, and sanitizer levels, are crucial for maintaining optimal water quality.
Using specialized chemicals, like algaecides and clarifiers, can effectively address common pool issues such as algae growth and cloudy water.
Importance of Pool Water Chemistry
Maintaining balanced water chemistry prevents damage to pool surfaces and equipment. When the water is not properly balanced, it can become corrosive or cause scaling, both of which are harmful to your pool’s longevity and aesthetics. Proper water chemistry enhances the effectiveness of sanitizers, especially chlorine, keeping your pool clean and safe.
Ideal pH levels ensure swimmer comfort and equipment protection. Extremes in pH can cause skin and eye irritation and damage pool surfaces and equipment. Regular monitoring of chemical levels keeps the water safe for swimmers and ensures effective sanitation. It’s not just about keeping the water clear; it’s about ensuring a pleasant and safe swimming experience for everyone.
Rainfall and heavy pool usage can significantly affect water chemistry. For instance, rainwater can dilute the pool’s chemical levels, while heavy usage can introduce contaminants like body oils and sunscreen. Irregular adjustments can lead to unhealthy chemical fluctuations, wasting money and causing health risks like algae infestation or the need to drain the pool.
Balancing pool water chemistry is crucial. It prevents corrosion, avoids skin and eye irritation, and protects the pool from damage. Proper water chemistry is the cornerstone of effective pool maintenance, ensuring safety and enjoyment for everyone.
Essential Pool Chemicals and Their Functions
Understanding the various chemicals involved is key to maintaining a clean and healthy swimming pool. The main chemicals needed include:
Sanitizers
pH adjusters
Alkalinity increasers
Calcium hardness increasers Each chemical plays a crucial role in keeping the pool water balanced and safe for swimmers.
Pool chemistry refers to the chemical condition of swimming pool water, which is critical for keeping it safe and enjoyable. Sanitizers like chlorine kill bacteria and algae, while pH adjusters maintain ideal pH levels for swimmer comfort and equipment protection. Additionally, understanding pool chemical balance is essential for optimal maintenance.
Alkalinity increasers stabilize pH levels, and calcium hardness increasers prevent damage to pool surfaces by maintaining appropriate water hardness. Understanding these chemicals and their functions is the first step in mastering pool care.
Sanitizers
Sanitizers keep pool water free from bacteria, viruses, and algae. Chlorine, the most common pool sanitizer, oxidizes contaminants and destroys them. An ideal chlorine level of around 3 ppm ensures effective pool sanitization, as chlorine sanitizes without irritating swimmers.
Other sanitizers, such as bromine and biguanide, are also used. Bromine’s longer active life makes it a good alternative for pools with higher water temperatures. Biguanide is a chlorine-free sanitizer that clumps contaminants for easier removal by filters.
While each sanitizer has unique advantages, chlorine remains the most widely used due to its effectiveness and availability.
pH Adjusters
The ideal pH level for pool water is between 7.4 and 7.6. Maintaining this range ensures water quality. Important considerations include:
Rainwater, swimmers, and contaminants can affect pH levels, so regular monitoring and adjustment are necessary.
High pH levels reduce chlorine effectiveness and lead to mineral deposits.
Low pH makes water corrosive, damaging finishes and equipment.
Use pH increasers and decreasers to manage pH levels. A pH increaser, typically sodium carbonate, raises pH levels, while a pH decreaser, usually containing muriatic acid, lowers them. Proper chemical balance ensures swimmer comfort and protects your pool’s surfaces and equipment.
Alkalinity Increaser
Correct alkalinity levels stabilize the pH in pool water. Total alkalinity buffers pH fluctuations, ensuring stable water chemistry. The recommended pool alkalinity range is 80 to 150 ppm, with some experts suggesting 80 to 120 ppm.
To manage alkalinity levels:
Use an alkalinity increaser to raise alkalinity.
Baking soda is another option to increase alkalinity.
Adjust alkalinity slowly and take multiple measurements to avoid overshooting.
If alkalinity is too high, add a pH decreaser to balance levels.
Keep a supply of alkalinity increaser as levels can fluctuate easily.
Calcium Hardness Increaser
Calcium hardness measures pool water softness or hardness, influencing its corrosiveness. Inadequate calcium levels can damage plaster and other surfaces. Low calcium hardness can lead to corrosion of pool surfaces.
The ideal calcium hardness level is between 175 ppm and 225 ppm for most pools, and 200 ppm to 275 ppm for concrete and plaster pools. High calcium hardness can lead to cloudy water and scaling, which is outside the acceptable range.
Increase calcium hardness using a calcium hardness increaser like calcium chloride. Proper calcium hardness levels prevent pool damage and ensure clear water.
Testing Your Pool's Water
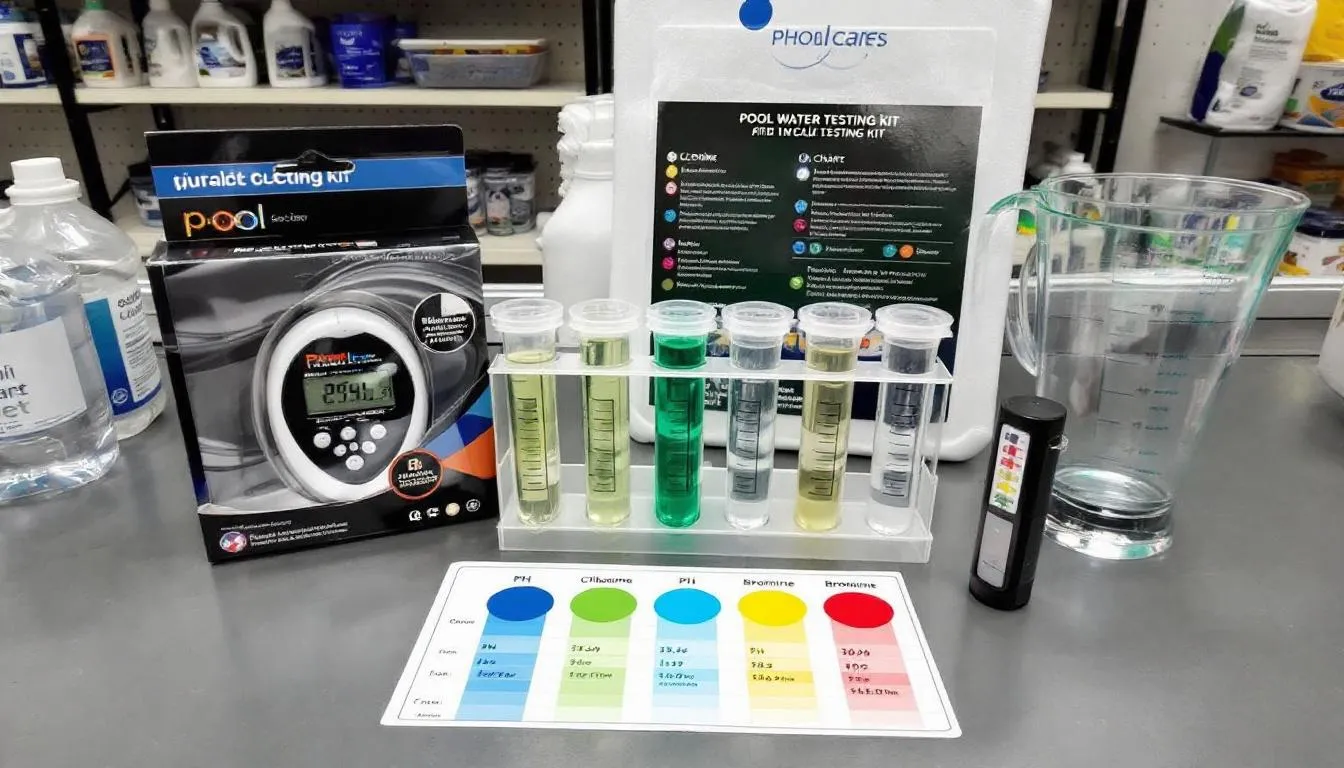

Regularly monitor your pool’s chemical levels to maintain optimal water quality. Test pool water chemistry using test strips, liquid test kits, or digital testers. Each method has its advantages; choose based on preference and required accuracy.
Weather conditions, usage patterns, and chemical additions influence how often to test pool water. Test for total alkalinity, total dissolved solids (TDS), and calcium hardness after rain showers or heavy pool usage.
Regular testing ensures chemical balance, keeping your pool safe and enjoyable.
Test Strips
Test strips provide a quick and straightforward way to assess pool water chemical levels. They give instant readings of water parameters like total chlorine, pH, and alkalinity.
Regular pH testing prevents swimmer discomfort and equipment damage, and it is essential to adjust pH.
Liquid Test Kits
Liquid test kits offer more accurate and precise results compared to test strips, ideal for pool maintenance. Collect a water sample in a clean container to use a liquid test kit, ensuring it represents overall water chemistry.
Start by listing some forbidden forms of the keyword “add chemicals” according to the rule 5. Follow the kit’s instructions to add chemicals and observe color changes to analyze chemical levels. Refer to the color chart to interpret results accurately.
Clean your testing equipment thoroughly after use to maintain accuracy.
Digital Testers
Digital testers offer a modern solution for precise pool water testing. They require minimal user input and display results on a screen for easy reading. Digital testers offer accurate readings, making them a reliable choice for pool owners seeking precision and convenience.
Balancing Pool Water Chemistry

pH, alkalinity, and calcium hardness are key elements for pool water balance. Using essential pool chemicals properly keeps water clear and safe for swimming. The pool’s alkalinity in pool water resists pH changes; the recommended level is 80 to 120 ppm. Maintaining saltwater pools requires attention to pH levels and calcium buildup, which are more pronounced than in traditional pools.
To keep water balanced in a saltwater pool:
Regularly check pH, chlorine, and calcium hardness levels.
Use the right chemicals to maintain proper chemical balance.
Perform regular testing and adjustments to prevent issues like algae growth, corrosion, and scaling.
These steps help keep your pool clean and safe.
Adjusting pH Levels
The CDC provides guidelines for residential pools. They recommend a pool’s pH level between 7.2 and 7.8. To increase pH levels, add sodium carbonate (soda ash). Proper pH levels are crucial for water chemistry and swimmer comfort.
Managing Alkalinity
Maintain total alkalinity between 110 to 150 ppm for stable pH levels. Low alkalinity risks corrosion and damage, making the pool unsafe for swimming.
Increase pool alkalinity by adding diluted sodium bicarbonate (baking soda).
Controlling Calcium Hardness
Calcium hardness prevents pool water from damaging surfaces or causing cloudiness. Excessive calcium hardness causes scaling and cloudy water. Maintain calcium hardness between 175 ppm and 225 ppm for most pools, and 200 ppm to 275 ppm for concrete and plaster pools.
If calcium hardness exceeds 400 ppm, drain and refill the pool to restore balance. Proper calcium hardness levels prevent pool damage and ensure clear water.
Shocking Your Pool

Shocking the pool keeps water clean, remedies algae, and addresses bodily mishaps. It helps to eliminate combined chlorine in pool water by raising the free chlorine level, contributing to a cleaner and safer swimming environment. To achieve breakpoint oxidation, the chlorine level must be 10 ppm higher than the combined chlorine reading. This ensures effective oxidation. Free chlorine kills bacteria, while combined chlorine is the chlorine used up that should be shocked. Using shock products that contain calcium can increase the calcium hardness level in the pool. This change occurs gradually over time.
Shocking your pool is crucial for eliminating bacteria, algae, and other contaminants, ensuring safe swimming conditions. There are various types of pool shock products available, including chlorine-based and non-chlorine options, each with unique properties and applications. Understanding when and how to shock your pool is vital for maintaining water quality and swimmer safety.
Types of Pool Shock
Calcium hypochlorite shock is a recommended type of shock for pools. Non-chlorine shock options, like potassium monopersulfate, serve as alternatives but are less powerful for algae.
Knowing the types of pool shock available allows you to choose the best option for your pool’s specific needs.
When and How to Shock Your Pool
Shocking your pool should be done regularly to maintain water quality. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific shock product you’re using. Generally, shocking should be done at night or when the pool is not in use to allow the chemicals to work effectively without interference from sunlight or swimmers.
Ensuring a proper chemical balance and using shock treatments as needed will keep your pool clean and safe.
Specialized Pool Chemicals
Specialized chemicals can target specific pool issues, enhancing overall water quality. These chemicals help in addressing problems like algae growth, cloudy water, and metal staining, making them indispensable for comprehensive pool maintenance. Using specialized chemicals can significantly improve the efficiency of pool maintenance by targeting specific water quality issues.
Silver and copper are minerals used in pool systems to sanitize water, though they work slower than chlorine. Knowing when and how to use these specialized chemicals can make a big difference in maintaining a pristine and inviting pool.
Algaecides
Algaecides can be categorized into preventative and curative types, with different applications for each. Preventive measures against algae include maintaining optimal chlorine levels and using algaecides as needed. Use a copper-free algaecide if your pool water is hard and contains high levels of minerals.
Algaecides are essential for preventing and treating algae, ensuring your pool remains clear and safe.
Clarifiers and Flocculants
A pool clarifier clears cloudy water by combining particles for easier pool filter removal. A pool flocculant grabs tiny particles, clumping them together to sink to the bottom for easy vacuuming. While clarifiers treat the symptoms of cloudy water, flocculants address the underlying causes, making both useful in pool maintenance.
These chemicals are crucial for maintaining clear water and ensuring an enjoyable swimming experience.
Metal Sequestrants
Metal sequestrants play a crucial role in preventing stains caused by metals in the water. Iron and copper are the primary metals that can cause staining in pools. If metals come out of solution in pool water, they can attach to pool walls and cause unsightly stains.
Using a metal remover or stain and scale remover can effectively manage metals in pool water, prolonging the life of pool surfaces.
Maintaining Saltwater Pools
Salt chlorine generator sanitize pool water by converting salt into chlorine via electrolysis. This process not only reduces maintenance time but also provides silky-soft water, enhancing the swimming experience. Composite fiberglass swimming pools are designed for salt chlorination, making them an ideal choice. However, it’s crucial to verify your salt cell every three months for buildup and clean it if necessary.
Weekly maintenance tasks for saltwater pools include skimming, brushing, and vacuuming the pool to keep it clean. When adding salt, it’s essential to run the pump to help distribute it evenly throughout the pool. Salt should typically be added to the pool once or twice a year or after significant rainfall to maintain appropriate salinity levels. Regular testing for free chlorine levels is recommended to ensure proper sanitation in the pool.
In vinyl-liner pools, salt chlorination can lead to metal surfaces rusting. This can pose potential problems. Concrete pools may require more frequent and costly resurfacing if using salt chlorinators. Despite these challenges, proper maintenance and regular checks can help keep your saltwater pool in excellent condition.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Water that is not properly balanced can cause several issues:
It can become corrosive or cause scaling, both of which are harmful.
Low alkalinity increases the risk of corrosion and makes the pool unsafe for swimming.
High levels of total dissolved solids can impair water clarity and may necessitate partial water replacement.
Using metal sequestrants regularly can prolong the life of pool surfaces by preventing metal-related damage.
Common issues like cloudy water, algae growth, and high cyanuric acid levels can be addressed with the right chemicals and maintenance practices. Flocculants are often used after heavy rainfall or pool usage to quickly clear up murky water. Regular monitoring and prompt action can prevent these issues from escalating, ensuring a safe and enjoyable swimming environment.
Cloudy Water
The most common cause of cloudy pool water is low chlorine levels. Inconsistent management of water chemistry can cause cloudy water. This issue can arise from improper balancing of chemicals. To clarify cloudy water, maintain proper chlorine levels and ensure consistent water chemistry management.
Regular testing and adjustments are crucial to keep the water clear and inviting.
Algae Growth
Algae increases slip risks, clogs filtration systems, and creates an environment conducive to harmful bacteria. To treat an existing algae bloom in a pool, shock the pool, possibly using double or triple shock depending on the type of algae.
Preventive measures like maintaining optimal chlorine levels and using algaecides can help prevent algae and kill algae while requiring more chlorine at bay.
High Cyanuric Acid Levels
Excessive cyanuric acid can lead to ineffective chlorine sanitization, making it essential to monitor and adjust levels. The ideal level of cyanuric acid in pool water is 100 ppm. It should not exceed this amount. If too much cyanuric acid builds up in pool water, you should dilute the water by replacing some with fresh water.
A cyanuric acid reducer can also be used to help lower high cyanuric acid levels. If cyanuric acid levels are too high, it may be necessary to drain the pool completely.
Summary
Mastering pool care involves understanding the importance of water chemistry, using the right chemicals, and regularly testing and adjusting your pool’s chemical levels. By maintaining a proper chemical balance, you can prevent damage to your pool surfaces and equipment, ensure swimmer comfort, and keep your pool clean and safe. Regular maintenance and prompt action can prevent common issues like cloudy water, algae growth, and high cyanuric acid levels. With the right knowledge and tools, anyone can become a pool chemistry expert and enjoy a pristine and inviting swimming pool.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is maintaining pool water chemistry important?
Maintaining pool water chemistry is essential because it protects your pool from damage, improves sanitizer effectiveness, and ensures a comfortable swimming experience. Taking care of these aspects keeps your pool inviting and safe for everyone!
What are the essential chemicals needed for pool maintenance?
To keep your pool in top shape, focus on sanitizers, pH adjusters, alkalinity increasers, and calcium hardness increasers. Maintaining these essential chemicals will ensure your pool remains clean and enjoyable all season long!
How often should I test my pool water?
You should test your pool water at least once a week, and more frequently after heavy use or rain to keep the chemical balance just right. Staying on top of your testing will ensure a safe and enjoyable swimming experience!
What should I do if my pool water becomes cloudy?
To clear up cloudy pool water, focus on maintaining proper chlorine levels and regularly managing your water chemistry. Taking these steps will keep your pool sparkling!
How can I prevent algae growth in my pool?
To prevent algae growth in your pool, maintain optimal chlorine levels and use algaecides when necessary. By staying proactive, you can keep your pool crystal clear and inviting!

